
Subjective personal pronouns are used to replace the subject in a sentence they are “I,” “you,” “he,” “she,” “we,” “they,” and “it.”.To continue our previous example, saying “She needed something, so she said she would go get it” is confusing. For example, the sentence “Sally needed bread, so she said she would go to the store to get it” contains three pronouns: two uses of “she” and one use of “it.” That sentence is a lot less awkward than “Sally needed bread, so Sally said Sally would go to the store to get bread.” It’s important to note that if you are going to use a pronoun, you must make sure you have already identified the noun it will replace in the sentence. It’s a good idea to use pronouns at times to help avoid repetitiveness in your writing. For example, “moose” doesn’t become “meese” and “café” doesn’t become “caves.” Learning to spot these special cases takes time and practice. However, some nouns don’t change (e.g., “sheep” and “series”) and some don’t follow the rules above. If the noun ends in -on, change the -on to -a (e.g., “criteria”).If the noun contains -oo, change the -oo to -ee (e.g., “teeth”).If the noun ends in -us, change the -us to -i (e.g., “stimuli”).

These nouns are used to describe general places, things, etc.

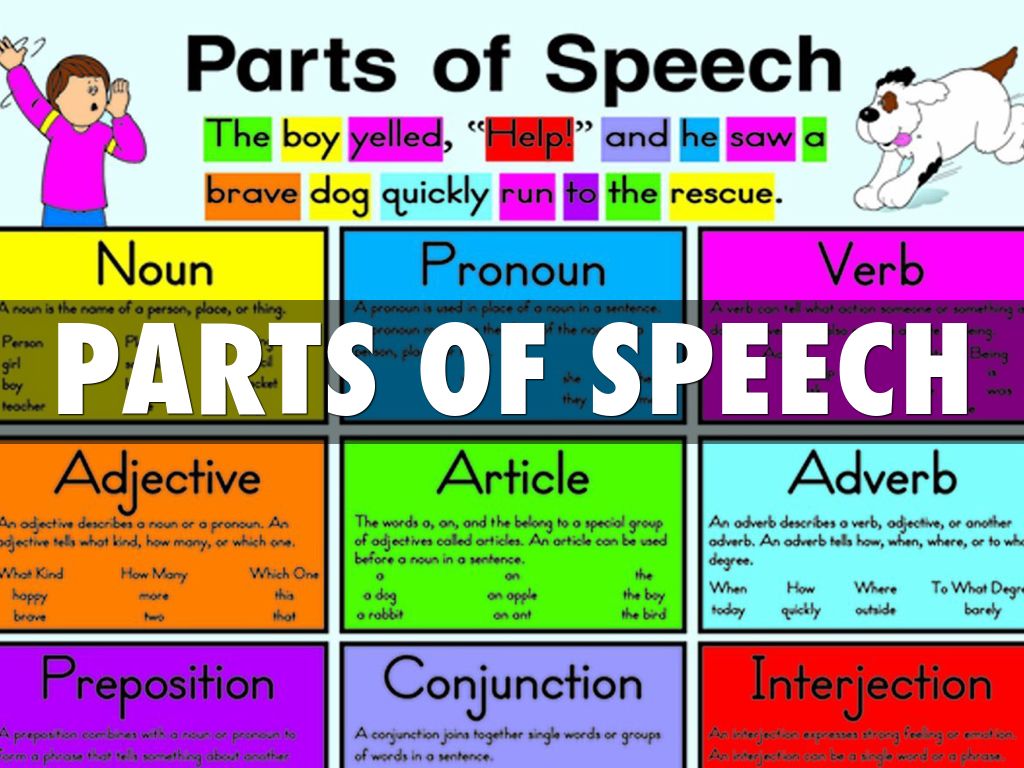
A proper noun is the name of a specific person (e.g., John) or a place (e.g., New York).Nouns are used for a person, place, thing, quality, activity, idea, or feeling. Below you’ll find a list of the different parts of speech, an explanation of what each part does, and some examples and helpful tips.Įnglish uses nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, and conjunctions.
PARTS OF SPEECH HOW TO
Basic English parts of speech When learning English grammar, it’s important to know about the different parts of speech that make up the language so you can understand how to communicate clearly and effectively.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
